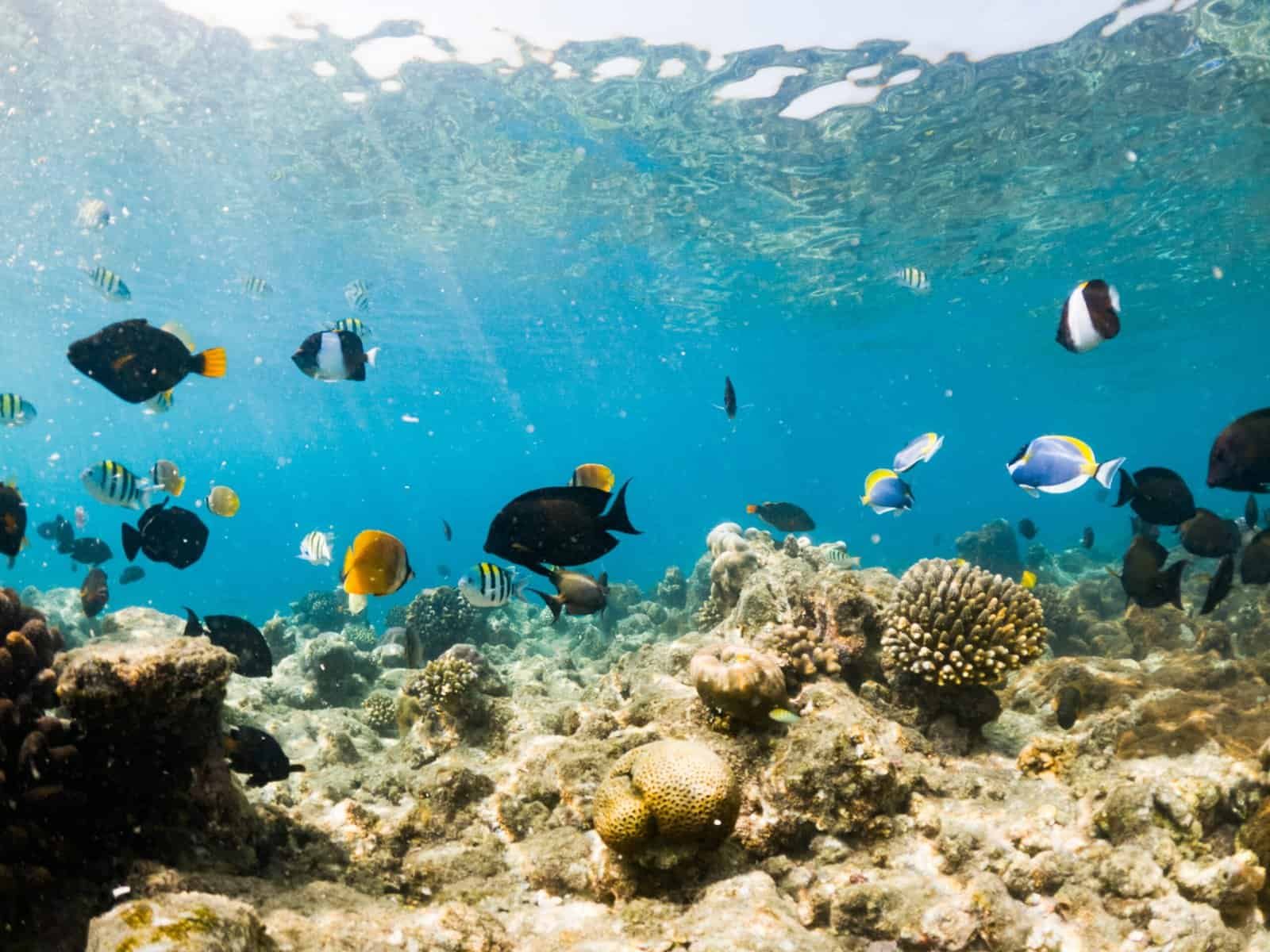
SDG 14: Life Below Water
Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources for sustainable development.
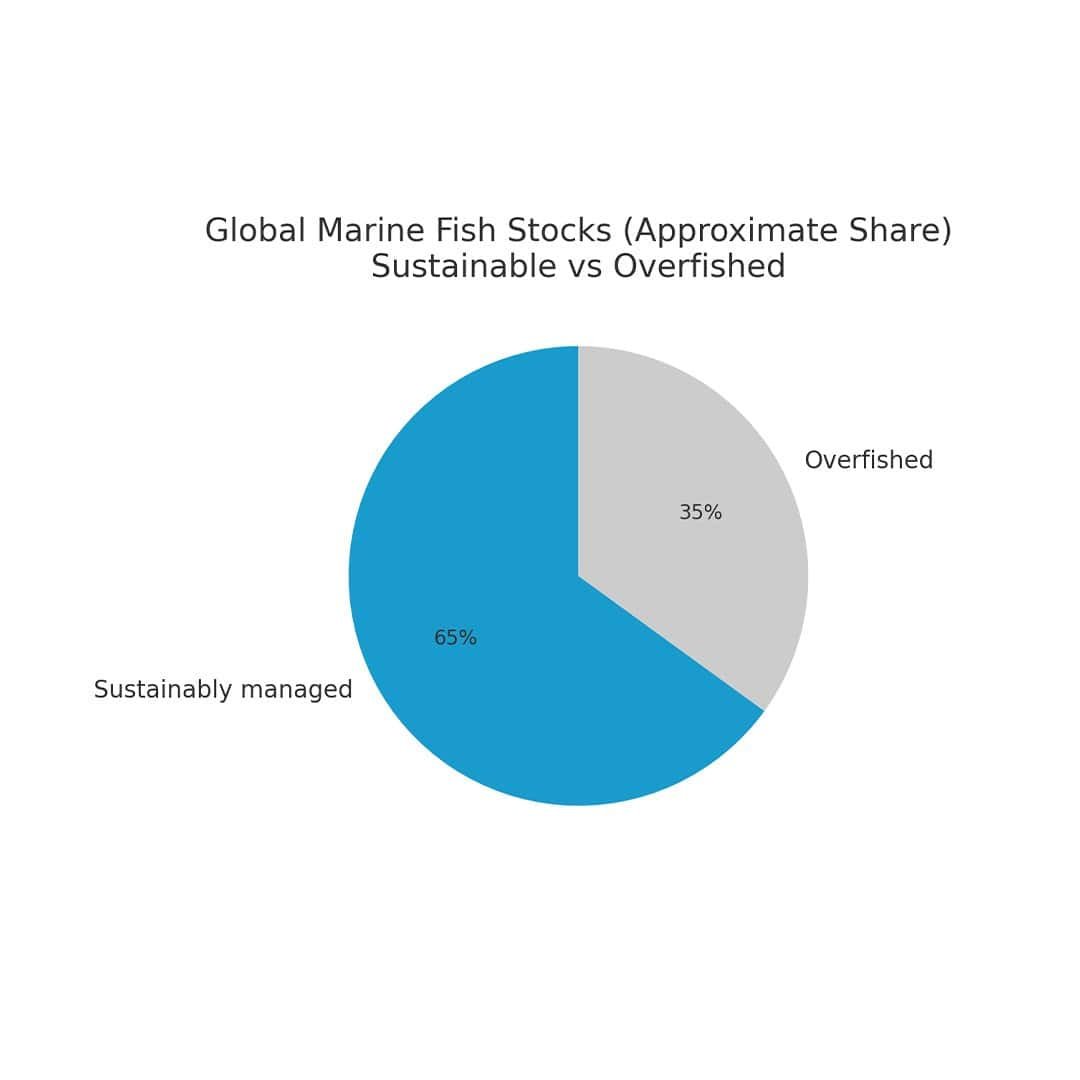
35%
of global fish stocks are overfished.
90%
of coral reefs are expected to be threatened by 2050 due to warming, acidification, and pollution.
Nearly 700
marine species have been documented as affected by plastic pollution.
About Goal 14
SDG 14 focuses on protecting oceans through reduced pollution, sustainable fishing, and healthy marine ecosystems. It supports conservation, restoration, and responsible resource use.

Focus Film
Action in Motion
Watch how we are driving change. Click play to learn more about our specific initiatives for this goal.
Partner Impact Stories
Discover how our global partners are contributing to this specific Sustainable Development Goal through innovation and local action.
Key Targets
- Prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, especially from land-based activities.
- Protect and restore coastal and marine ecosystems to strengthen their resilience and support biodiversity.
- Reduce ocean acidification by enhancing scientific cooperation and improving monitoring.
- Regulate harvesting, end overfishing, and implement science-based management plans to restore fish stocks.
- Conserve at least 10% of coastal and marine areas through effective and equitable marine-protected areas.
- Prohibit harmful fisheries subsidies that contribute to illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing.
- Increase economic benefits to small island developing states and least developed countries through sustainable marine resource use.
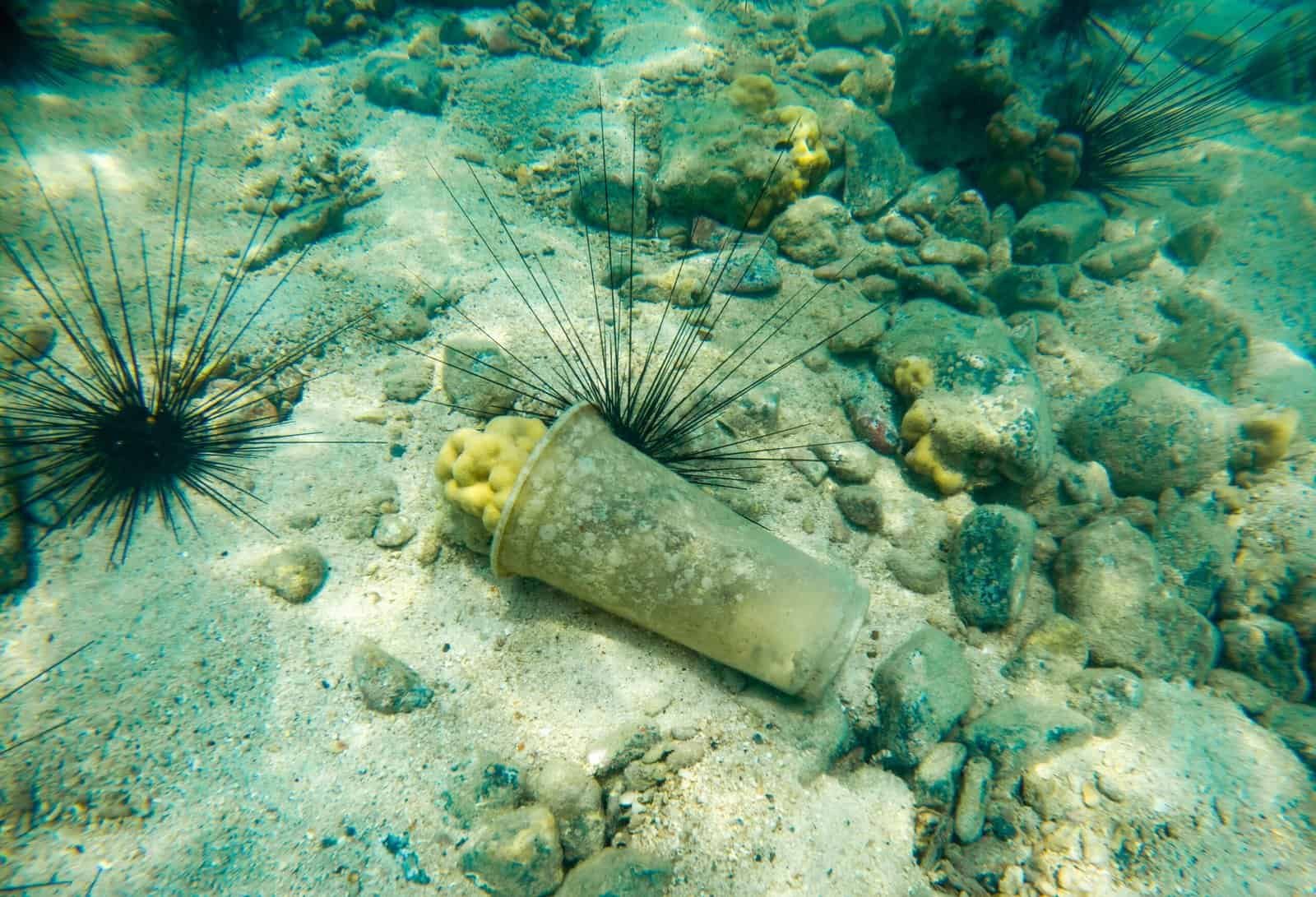

Global Progress
Progress on SDG 14 is mixed. Marine pollution and overfishing remain severe, and climate change harms coral and coastal ecosystems. Protected areas and monitoring improved in some regions, but stronger global action is needed.
Explore Other Goals
1
SDG 1: No Poverty
2
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
3
SDG 3: Good Health
4
SDG 4: Quality Education
5
SDG 5: Gender Equality
6
SDG 6: Clean Water
7
SDG 7: Affordable and clean energy
8
SDG 8: Decent Work
9
SDG 9: Industry & Infrastructure
10
SDG 10: Reduced Inequality
11
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities
12
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption
13
SDG 13: Climate Action
15
SDG 15: Life on Land
16
SDG 16: Peace & Justice
17
SDG 17: Partnerships





